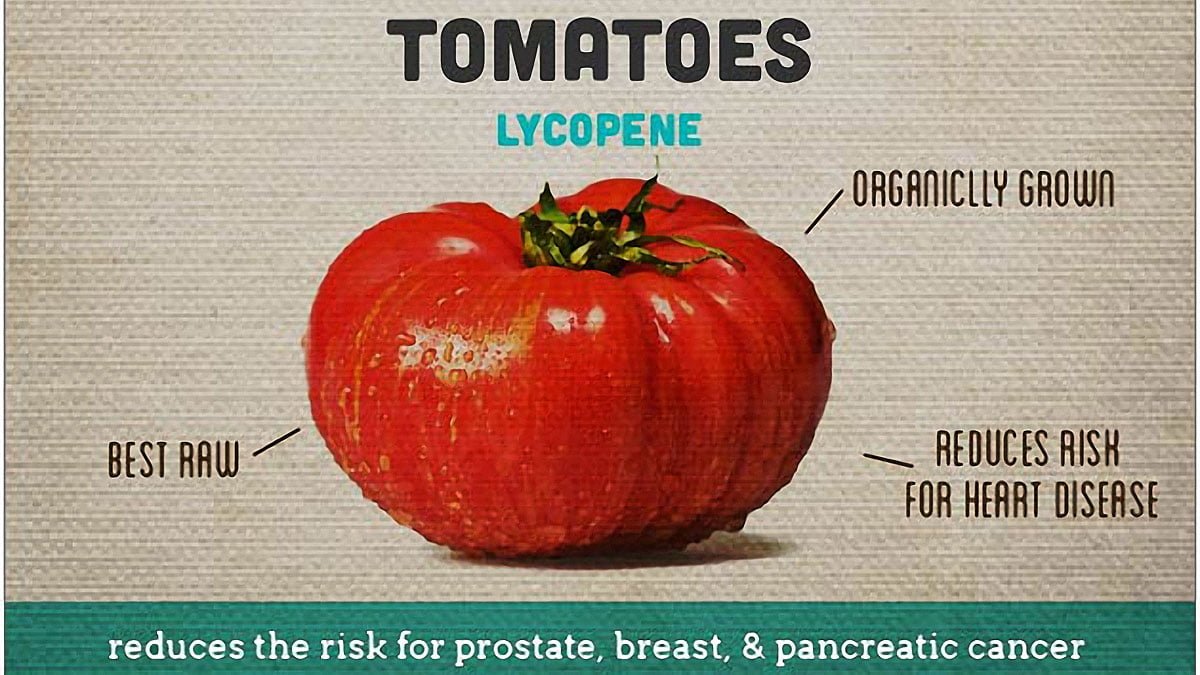
1. Tomatoes
Tomatoes are an excellent dietary source of lycopene, a phytochemical molecule known as a carotenoid, which is responsible for the vibrant red, orange and yellow colours of a lot of vegetables and fruits. Lycopene is probably the carotenoid which has potentially the most powerful impact on the fight against cancer.[1]
Although most studies on the tomatoes’ anticancer effects focused on prostate cancer prevention, it appears likely that tomatoes could play a role in preventing other cancers.
Cooked tomato products are especially rich in lycopene. Exposure to heat ruptures the cell walls which allow the molecule to be better extracted, bringing about changes in the structure letting it be more easily assimilated by the body.[2]
Consuming tomato-based products is an easy way to help reduce prostate cancer risk. Eating 2 tomato sauce-based meals each week could lower prostate cancer risk by a remarkable 25%.